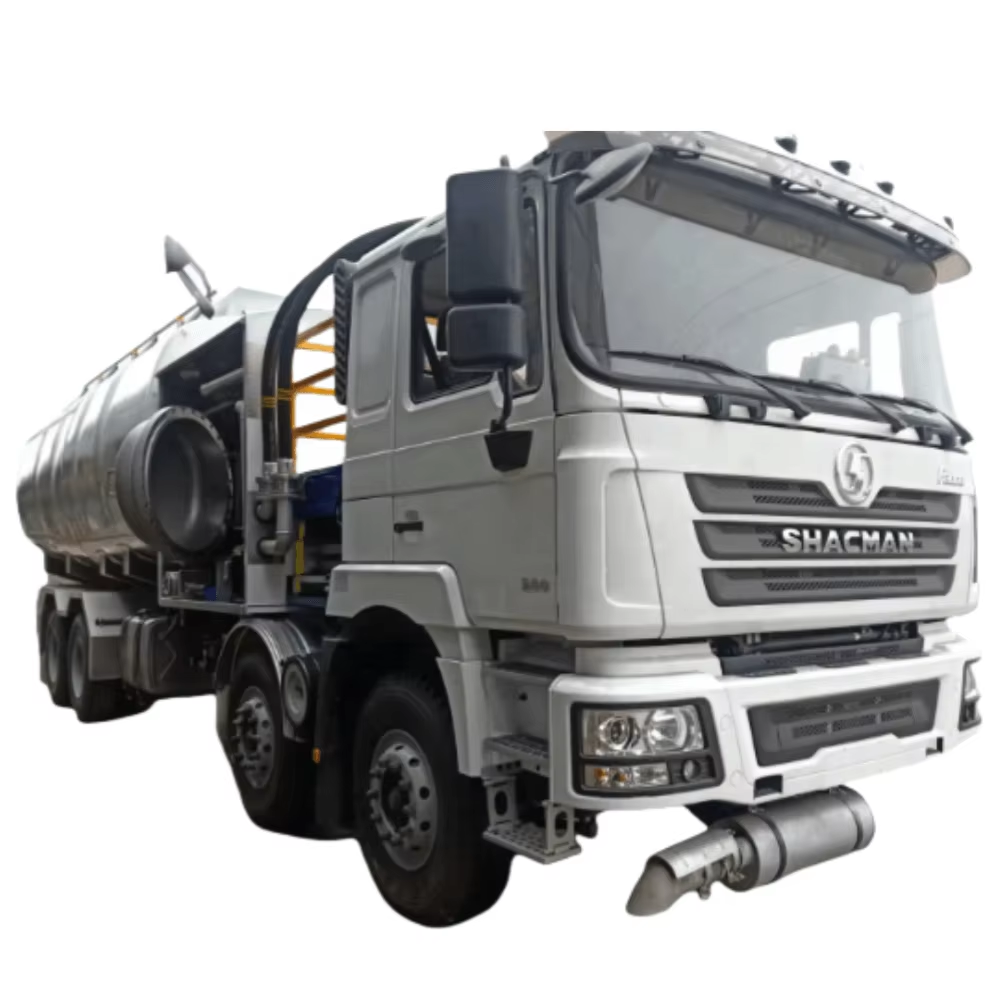
Aviation Refueling Trucks: Key Selection Factors
Matching Truck Capabilities to Aircraft Requirements
Matching aviation refueling trucks to what different planes actually need makes all the difference when it comes to getting things done efficiently. Aircraft come in all shapes and sizes, so their fuel requirements vary quite a bit. Small private jets might only need around 2,000 liters while massive cargo planes could want upwards of 200,000 liters. That means knowing exactly what kind of work each plane does matters a lot. When there's a mismatch between what the fuel truck offers and what the aircraft needs, problems start popping up. Industry folks have seen this happen time and again where deliveries take forever or costs balloon out of control. Choosing the right truck for the job isn't just smart business it's practically necessary if operations are going to run smoothly day after day.
Flow Rate Efficiency Across Different Aircraft
How fast fuel flows through the system really affects how long it takes to refuel planes and get them back into service, which matters a lot for keeping airports running smoothly. Most folks in aviation know what kind of numbers to expect when it comes to fuel flow rates. Small planes generally need around 100 liters per minute while bigger jets can guzzle up to 3,000 liters per minute during refueling. Research shows that getting those flow rates right means shorter waits on the tarmac, which saves money in the long run and keeps services running better than they would otherwise. Aviation tankers that hit these target flow rates help airlines save cash while making their schedules more reliable and keeping more aircraft ready for action when needed.
Critical Ground Clearance Considerations
The amount of ground clearance really matters when it comes to safely operating aviation refueling trucks around airports with different kinds of terrain and sometimes even off-road areas. Airport operations face all sorts of challenges depending on where they're located. Some places have perfectly flat runways while others deal with rough patches, potholes, or construction zones that can trip up equipment. The required ground clearance actually changes based on what kind of plane we're dealing with. Smaller business jets typically don't need much adjustment at all, but those big wide-body aircraft definitely need more space underneath to avoid damaging their landing gear systems. We've seen plenty of real world examples where proper ground clearance adjustments made a huge difference. Airports in mountainous regions or older facilities with irregular pavement reported fewer breakdowns and better overall performance after making these modifications. Getting this right isn't just about following specs it's about keeping things running smoothly no matter what kind of surface conditions mechanics might encounter day to day.
Essential Technical Specifications
Fuel Capacity and Transfer Speed Requirements
The amount of fuel a truck can carry and how fast it transfers fuel matters a lot when talking about aviation refueling vehicles because these factors affect how well operations run day to day. Different parts of the aviation industry need varying amounts of fuel storage space. Small planes typically work fine with smaller tanks, but big commercial jets need much bigger ones so they don't have to stop multiple times during flights, something that definitely causes schedule problems. When it comes to transfer speeds, faster pumping means better workflow management since refueling gets done quicker without holding things up too long. Aviation regulatory bodies set standards for minimum fuel capacity based on what types of aircraft operators actually encounter in real world conditions. Getting this right helps keep flight schedules intact while also saving money on unnecessary fuel waste over time.
Filtration Systems for Aircraft Fuel Integrity
Keeping aviation fuel clean is absolutely critical for safe operations, and good filtration systems play a major role here. The filters take out stuff like dirt particles, water droplets, and other contaminants that might otherwise end up in airplane engines. Most fuel trucks used at airports have multiple filtration stages built into them micro filters catch tiny bits while water separators handle liquid contamination. Engineers working in aerospace have actually tracked this stuff pretty closely, and their research shows that planes experience far fewer problems when they get properly filtered fuel. Nobody wants to think about it, but bad filtration can really mess things up serious engine damage or even complete failures happen if contaminated fuel makes it through to the aircraft. That's why modern refueling equipment keeps getting better at separating out harmful substances before they ever reach the tank.
Chassis and Control Systems
The frame and controls on those big aviation refueling trucks really matter when it comes to getting the job done right. Truck manufacturers design different frames based on what they need to accomplish, which affects how well they move around and deliver fuel efficiently. Take those narrow spots at airports where space is super limited - special frames let these massive vehicles turn corners and maneuver through tight areas without causing problems. The control panels inside these trucks are just as important though. Good controls give pilots and ground crews better control over the refueling process, cutting down mistakes made by people and making everything faster while keeping everyone safer. We've seen some pretty cool tech developments lately too. Digital control systems now allow operators to monitor fuel flow much more accurately than before, plus these systems can actually predict when parts might fail so maintenance teams know exactly when something needs fixing before it breaks down completely.
Safety and Compliance Standards
Critical Aviation Fueling Safety Protocols
Safety must come first when handling aviation fuel to avoid any mishaps. The basic rules include checking all equipment thoroughly before starting, following established procedures step by step, and making sure the fuel meets quality requirements. When these safety measures get ignored, things can go very wrong indeed – we've seen accidents happen and airlines facing hefty fines from regulatory bodies. A recent IATA safety guide warns that failing to follow proper fueling protocols puts everyone at risk, from ground staff to pilots and passengers alike. Beyond just avoiding trouble with regulators, sticking to these standards makes good business sense too. Proper fueling practices keep aircraft ready for service and protect the bottom line in the long run.
International Regulatory Requirements
The rules governing aviation refueling come from places like the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). These groups set safety standards that help keep things consistent worldwide. But here's the catch – what works in one country might not fit another's needs exactly. Take the United States for example where FAA regulations demand strict follow through on every step of the process. Meanwhile ICAO takes a bigger picture approach looking at overall safety rather than minute details. Staying compliant means operators need to constantly watch for updates and adjust their operations accordingly. Most experienced professionals know this isn't just theory either; they've seen how changing regulations affect day to day work at airports around the globe.
Operator Safety Features
Safety features on aviation refueling trucks aren't just nice to have they're absolutely necessary for keeping everyone safe around those massive machines. Emergency shut off valves stop fuel flow instantly if something goes wrong, while overfill prevention systems kick in before tanks get dangerously full. Most modern refueling trucks built within the last decade come standard with these lifesaving components. The Aviation Safety Network actually did some research showing how these systems prevented several near misses at airports worldwide. Without them, we'd see far more dangerous situations developing during routine fuel transfers. For ground crews working daily with aircraft, knowing their equipment has reliable safety backups makes all the difference between a normal day and a catastrophe waiting to happen.
Specialized Applications
Fuel Tanker Trucks vs Hydrant Dispensers
Looking at fuel tanker trucks versus hydrant dispensers requires thinking about design differences, how efficient they are, and what situations work best for each. Tanker trucks move around and carry fuel straight to planes, which makes them great when there isn't much fueling equipment nearby. They can go wherever needed, pretty handy actually. Hydrant dispensers sit in one place connected to those underground pipes we see running across airport grounds. These let planes get fueled up fast right from the main fuel storage area. Smaller airstrips often rely on tankers because they need that mobility factor. Big international hubs like Heathrow have those big red hydrant lines everywhere since they handle so many massive jets daily. The difference really comes down to what kind of operation an airport runs. Some places just don't have room or budget for all those pipes, while others benefit huge from having everything hooked up permanently.
Military vs Commercial Refueling Considerations
Refueling planes in military settings brings different challenges than what we see in commercial aviation, particularly when it comes to the kinds of trucks involved. The military needs refueling equipment that can handle rough conditions, which means making serious modifications to standard designs so they work across all sorts of terrain and weather extremes. Specialized military fuel trucks typically come with heavy duty frames, upgraded suspensions, and sometimes even armor plating to keep them running safely during combat situations. Defense departments track these specs closely because getting fuel to aircraft quickly can literally mean the difference between success and failure on missions. On the other side of things, commercial airports care mostly about how fast they can get planes fueled up again. Take the Garsite 9800 model for instance it holds massive amounts of fuel while still moving quickly between gates. Operators who manage both military bases and civilian airports need to know these differences inside out to make smart decisions about their fleet requirements.
Jet Fuel Tanker Truck Adaptations
Tanker trucks designed for jet fuel need special modifications because regular fuel doesn't behave the same way when moving around in transport. Temperature management is a big deal since jet fuel reacts differently to heat changes, something that affects both how stable it stays and what happens if there's an accident during transit. The tanks themselves are built with materials that stand up against corrosion from jet fuel, keeping them functional longer without leaks or damage. Industry experts talk about these features all the time, particularly when talking about safety standards and how fuel quality holds up across various climates. Insulated lining inside the tanks plus good filtration systems help keep contaminants out while protecting the fuel itself. This matters a lot for planes taking off and landing safely day after day.